As investors, staying informed about economic indicators is crucial to making sound investment decisions. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is one such indicator, providing insights into the inflationary trends within the economy. Today, the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) released the CPI data for the June Quarter 2024.
Overview of the June Quarter 2024 CPI Data
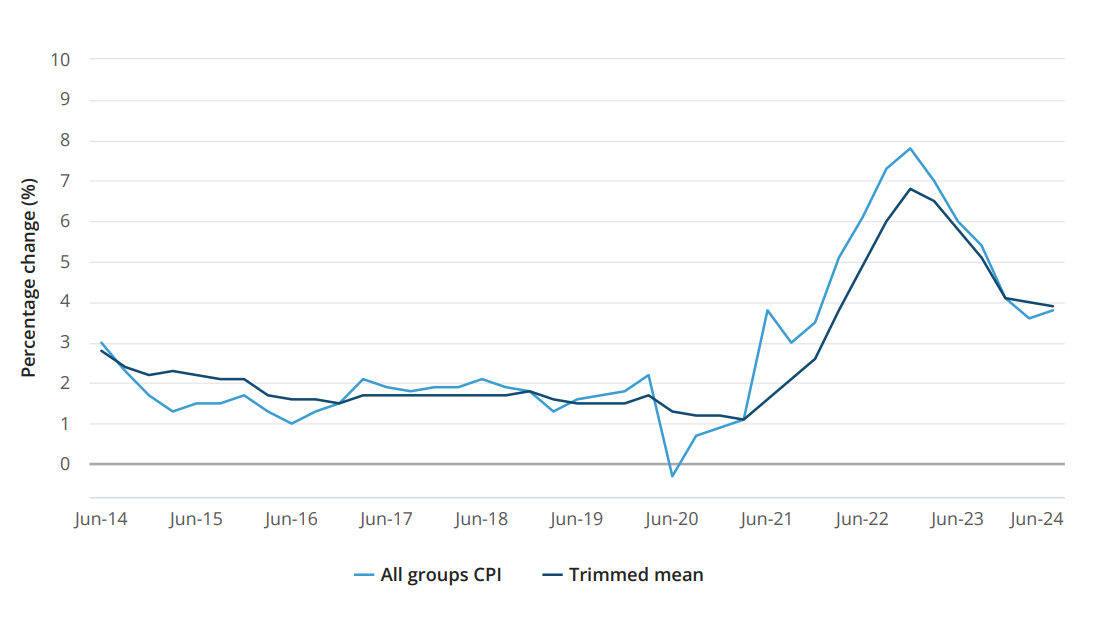
The CPI data for the June Quarter 2024 reveals a 1.0% increase in prices over the quarter and a 3.8% increase over the past twelve months. While this marks a continuation of the inflationary trend, the underlying details provide a nuanced view of the economic landscape.
Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics
Key Statistics and Detailed Analysis
The housing sector remains a significant driver of inflation. Prices in this category increased by 1.1% for the quarter and 5.2% over the year. The rise in housing costs was primarily driven by higher rents, which increased by 2.0% this quarter, reflecting strong demand and low vacancy rates. Additionally, new dwelling purchases by owner-occupiers rose by 1.1% due to higher labour and material costs. Electricity prices also saw a notable increase of 2.1%, influenced by the exhaustion of Energy Bill Relief Fund rebates.
In the category of food and non-alcoholic beverages, there was a 1.2% increase this quarter and a 3.3% rise over the year. Notable price movements included a significant rise in fruit and vegetable prices, up by 10.6% this quarter due to unfavourable growing conditions. Meals out and take away foods also increased by 0.6% quarterly and 4.2% annually, while non-alcoholic beverages rose by 1.1% this quarter.
The clothing and footwear sector experienced a 3.1% surge in prices this quarter and a 2.9% rise over the year. This increase was driven by new season stock and the end of promotional activities. Similarly, the alcohol and tobacco category saw a 1.5% quarterly rise and a 6.8% annual increase, primarily due to the biannual AWOTE indexation and residual impacts from the February excise increase.
Factors Contributing to Moderating Inflation
Despite these increases, some categories saw price decreases, helping to moderate overall inflation. Communication costs, for instance, decreased by 0.8% this quarter, although they remain 1.4% higher annually. This decline was primarily due to reduced costs in telecommunication equipment and services.
The furnishings, household equipment, and services category saw only a 0.8% increase this quarter and a -1.1% annual change, indicating some deflationary pressures. Additionally, domestic holiday travel and accommodation prices fell by 4.8% this quarter, contributing to lower overall inflation in the recreation and culture category.
Trends and Predictions
While the overall CPI indicates a continued rise in prices, underlying trends suggest a potential moderation in inflation. The trimmed mean, which reduces the effect of irregular or temporary price changes, rose by 0.8% this quarter, down from 1.0% in the previous quarter. Similarly, the weighted median increased by 0.8%, indicating a steadying of inflationary pressures.
Analysis of Non-Tradables vs. Tradables
Non-tradables, which are influenced primarily by domestic factors, remained high at 5.0% annual inflation. Key contributors included rents, which increased by 2.0% this quarter, medical and hospital services, which rose by 2.1%, and new dwelling purchases by owner-occupiers, which increased by 1.1%. On the other hand, tradables, affected by international trade, saw an annual inflation increase for the first time since September 2022. This rise was driven by high prices in automotive fuel, significant price increases in fruit and vegetables, and higher costs in clothing and footwear due to global supply chain issues.
Tamim’s Takeaways
Despite the overall rise in CPI, several indicators suggest that inflationary pressures might be moderating. The trimmed mean and weighted median show a reduction in the rate of inflation, indicating that the most volatile price changes are beginning to stabilise. Additionally, deflationary trends in categories such as communication and furnishings could offset rising costs in other areas. The significant drop in domestic holiday travel and accommodation prices might also reflect broader trends in discretionary spending, which could help moderate overall inflation.
Looking ahead, while housing and food prices remain high, the stabilisation in other categories suggests that the overall inflation rate may begin to decline in the coming quarters. Factors such as continued policy interventions, potential improvements in supply chains, and changes in consumer behaviour could all contribute to this moderation.