Author: Robert Swift
|
|
|
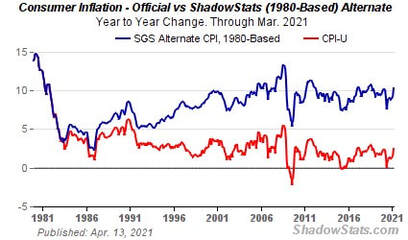
We also have an admission of sorts that inflation is here and, woops, higher than promised. Don’t wait for any apology. It’s not entirely the current Administration’s fault. The asymmetrical approach to interest rates, inflation and sound money in general started with ‘Maestro’ and has snowballed since.
Nonetheless a perverse sort of Gresham’s Law is applying here – bad policies continue to drive out good. Inflation is the new good thing and we should welcome it. Yet as Ronald Reagan said in 1978, “Inflation is as violent as a mugger, as frightening as an armed robber and as deadly as a hit man.”
Memories indeed are short.
We are potentially near the end of the liberal era of economic policy with which Regan and Thatcher were associated? Prepare for more government, more rules, and different risks.
Since none of us is going to be in charge of macro-economic policy (at least anytime soon) and we have to invest to maintain our spending power in real terms, against this backdrop of understated inflation and carefully massaged negative real interest rates, how should we proceed?
The answer is to look at certain equities as a better inflation hedge and also a hedge against risk of catastrophic corporate failure. Essentially then do not ignore equities even if you are at an ‘advanced age’ .
Conventional wisdom states that the allocation to fixed interest should rise as you get older. A rule of thumb is that you should have your age as a % in fixed income. So at 60, you should have 60% in bonds. At current levels of interest rates and inflation, this will almost certainly guarantee an erosion in real purchasing power. Don’t do it!
Two dimensions should be used to assess which are the better equities to currently overweight if you wish to buy inflation protection:- one is Governance as in “ESG” (which we think still improperly used); the other is sector membership and the stability of revenue growth and asset base.
Below we show how and why better Governed companies have a better survival rate and thus should have a lower discount rate applied to their dividends. These companies are still currently undervalued.
We then show that in the last 40 years, the risk of catastrophic loss in certain USA sectors has been much greater in some than others. Any investor with a time horizon beyond 5 minutes should thus weight their equity exposure to companies in these sectors.
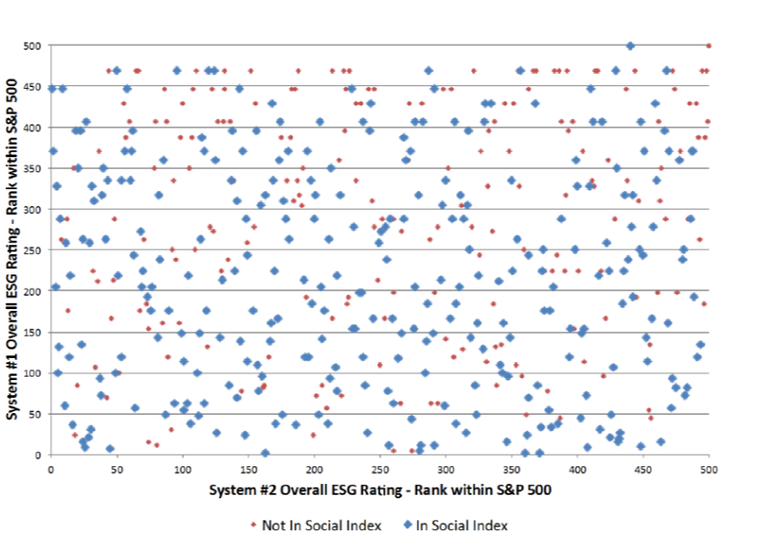
We have written before on ESG and why we think G is relevant as a risk factor but not necessarily as an alpha factor. We show again below the wide range of ESG cores from different ESG ratings agencies, courtesy of Northfield (no alignment).
This article provides a recent assessment of ESG scores and how they are barely useful.
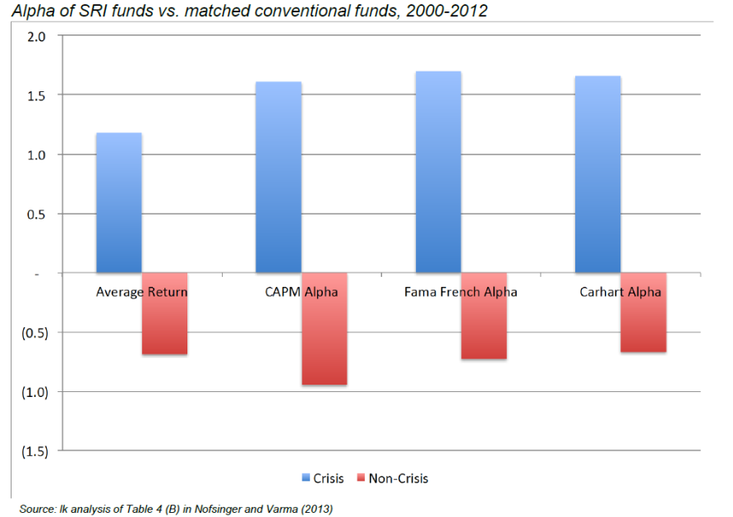
Nonetheless, good G as measured by its impact on corporate financials, IS useful. Sensible leverage, correct levels of re-investment, and staff retention are all part of any Fundamental or Qualitative assessment in deriving the correct discount rate to apply to a companies’ future earnings. Good G can produce lower discount rates through higher survival rates.
Below is some analysis of the performance of high G companies in a crisis. Think of it as built in downside protection to favour high G companies.
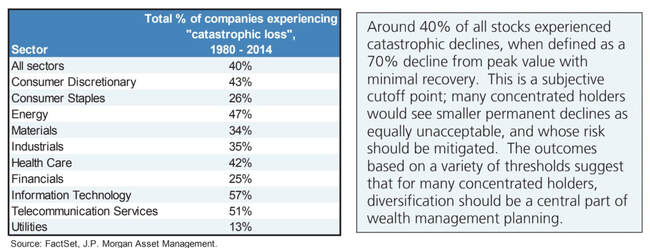
Sector membership matters too. It is always surprising to ask investors how long they think the average company lasts. It is not forever. Many companies fail and will continue to fail. Go back and watch any sporting event from 40 years ago. How many of the companies on the advertising billboards are still around today?
What really hurts compounding of returns is a catastrophic loss of capital; it only takes a few stocks to seriously fall for the poorly designed portfolio to suffer serious damage. So how to avoid this risk? Check out the table below:
Companies meeting these criteria are priced and behave as “index linked corporate bonds”. In this regard they are unique. They provide a decent yield compared to the pitifully low or even negative rate on ‘safe’ government bonds and the current yield on index linked bonds which of course is negative; AND they offer a measure of hedge against inflation since equities are a claim on nominal growth which conventional bonds are not. Index Linked bonds do provide a hedge against inflation but with negative yields, they are expensive. Buying an index linked bond with a negative yield of 1.5% and not a utility company with a dividend yield of 4% is giving up annually, a 5.5% return.
Equities we own in this space include AES Corporation (AES.NYSE), Quanta Services (PWR.NYSE), Johnson Controls (JCI.NYSE), OneOK (OKE.NYSE), Enbridge (ENB.TSE), Terna (TRN.BIT), ENEL (ENEL.BIT), Rubis (RUI.EPA), General Mills (GIS.NYSE), Iron Mountain (IRM.NYSE), ENN Energy (2688.HKG), Verizon (VZ.NYSE).
We view this as getting a yield in line with corporate bonds, AND the index linking of an inflation proof bond. These companies will have a greater chance of survival in the long run if history is a guide. The chances of a policy mis-step are now high so this is the time to be thinking about survivor strategies.
Currently therefore we are overweight Utilities, Infrastructure and Industrials. Given their superior survival characteristics, their lower P/E multiples and higher dividend yields they look attractive, Add in the likely buying frenzy to be unleashed as other investors scramble to get behind the newly discovered infrastructure spending plans in the USA and Europe, the best place to have risk would appear to be in these companies rather than the now very vulnerable to regulation, non tax paying, non-voting share class issuing, expensive stocks of yesteryear.
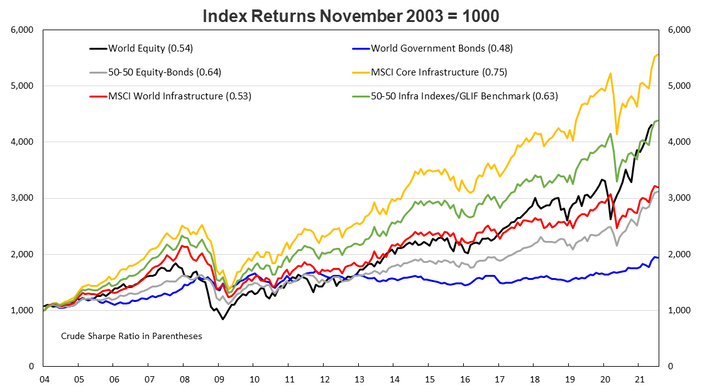
Lastly here is a slide of returns over the last 18 years accruing to equities, government bonds, infrastructure equities and blends of each. Even during this period of ‘growth’ equity excitement, one didn’t lose out too much by having exposure to defensive stocks in sectors with high chances of surviving a shock.